The principle and function of steam trap
Steam trap is a common key component in steam systems. It is used to remove condensation water and other non-steam components in pipelines and maintain the normal operation of the system. It is based on the principles of thermodynamics and automatic machinery and has the following functions and characteristics.
First of all, the main function of the steam trap is to remove condensation water in the pipeline. In steam systems, as steam cools and condenses, large amounts of condensate are produced. If not removed in time, condensate will accumulate and affect steam transfer efficiency, and even cause equipment failure. Through the induction system and float mechanism, the steam trap can automatically detect and remove condensation water to maintain high efficiency and stable operation of the system.
Secondly, steam traps prevent steam leakage. When condensate accumulates in a steam system, it can clog pipes and valves, causing steam leaks. Through automatic sensing and control, steam traps can discharge condensate water in time to prevent leakage and ensure the safe operation of the system.
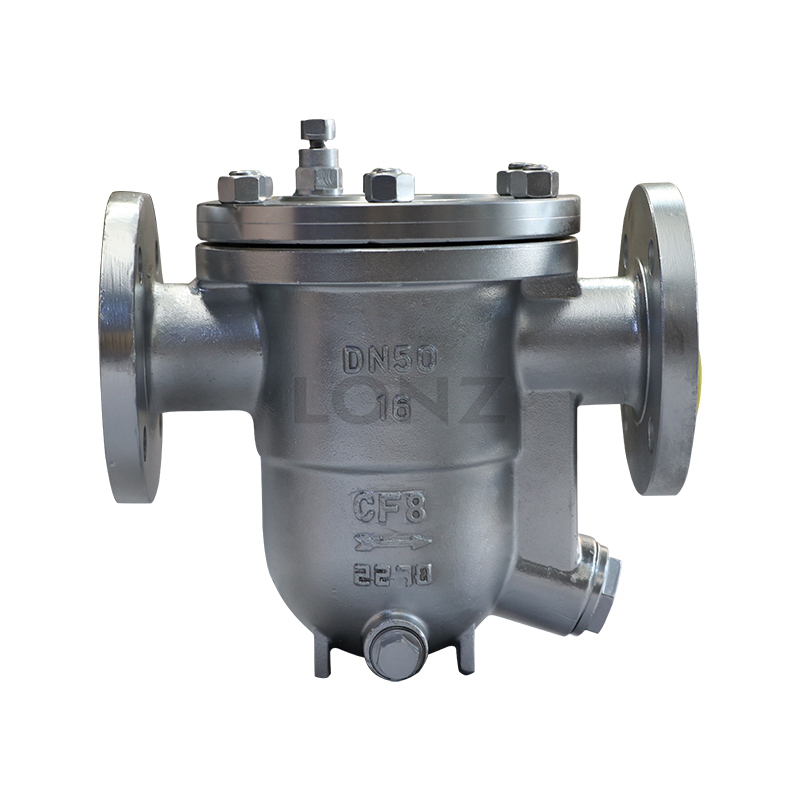

Additionally, steam traps prevent steam from overheating. When overheating occurs in the steam system, the steam trap will automatically open to discharge part of the overheated steam, reduce the temperature of the system, and maintain the stable state of the steam. This helps improve the thermal efficiency of the system and reduces energy waste.
Steam traps are widely used in various industrial fields. In large industrial systems such as power plants, chemical plants, and pharmaceutical plants, steam traps are often used for steam supply, steam transfer, and equipment protection. They have become an important part of ensuring the safe and stable operation of the system.
In summary, steam traps maintain the normal operation of the steam system by removing condensation water and preventing steam leakage and overheating. With their high efficiency and automatic characteristics, they play a key role in various industrial fields, improving system reliability and energy saving effects.